


bat365中文官网植物营养员工物学课题组联合佛山科学技术学院和德国波恩大学相关课题组在硼缓解酸性土壤铝毒抑制植物根系生长研究中取得新进展,相关成果1月31日以“Boron Supply Restores Aluminum-Blocked Auxin Transport by Modulation PIN2 Trafficking in the Root Apical Transition Zone”为题发表在Plant Journal上。
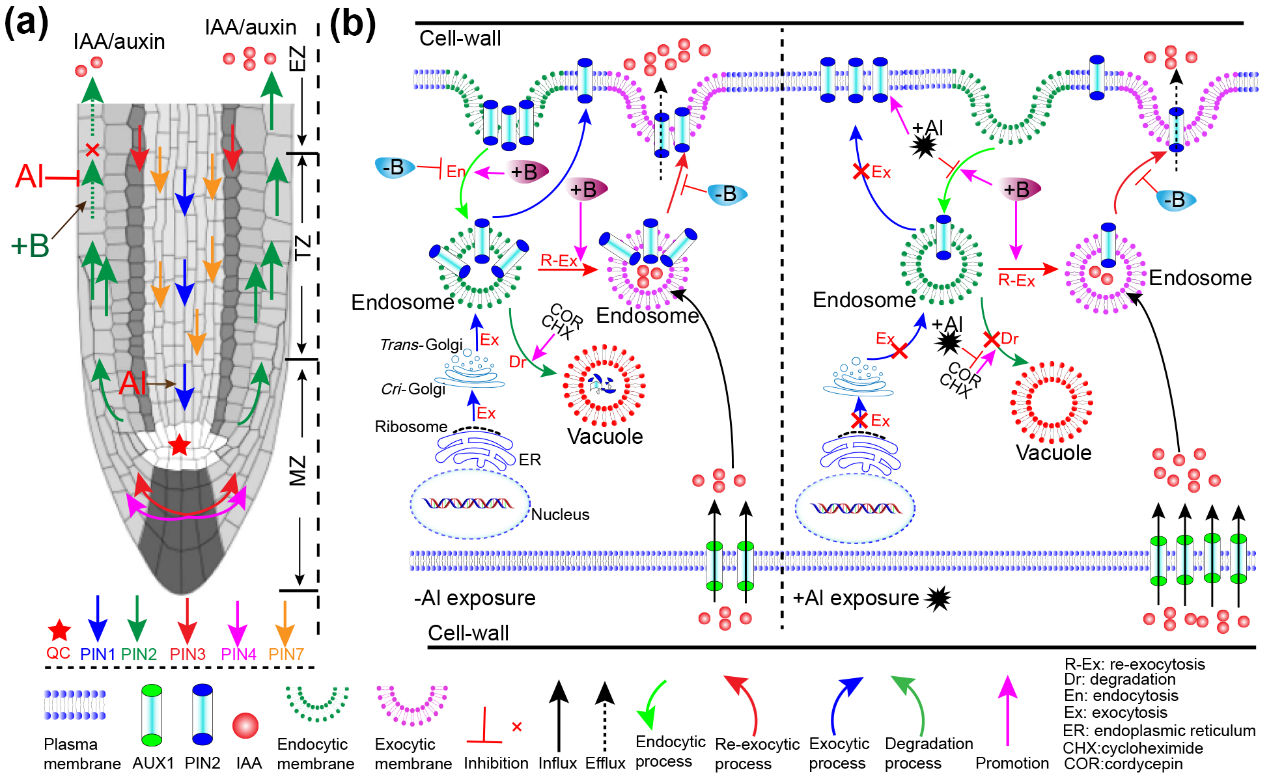
酸性土壤中,植物不仅遭受铝毒害,而且面临缺硼胁迫。前期研究发现硼缓解铝胁迫对根尖生长素运输抑制,但该机制尚不清楚。生长素(auxin,IAA)从地上部向根尖静止中心(quiescent center,QC)的运输依赖于定位在中柱和中柱鞘的PIN1/3/4/7载体蛋白协同作用。IAA从QC再分配到伸长区(elongation zone,EZ)主要依赖于表皮细胞膜PIN2载体蛋白。该研究利用共聚焦荧光显微镜观察转基因DII-VENUS和DR5-GFP株系发现铝胁迫诱导根尖分生区(meristem zone,MZ)和过渡区(transition zone,TZ)生长素积累,伸长区生长素含量减少,硼能缓解该过程。利用药物干扰及转基因材料PIN2-Dendra2实时观察铝胁迫和供硼对PIN2膜蛋白的影响,结果发现铝胁迫引起PIN2膜蛋白含量增加依赖于铝对PIN2膜蛋白内吞作用的抑制,而不依赖于PIN2基因转录调控。PIN2膜蛋白内吞和循环实验进一步证实供硼促进PIN2膜蛋白内吞和循环来缓解铝对PIN2囊泡运输的抑制。我们提出硼缓解铝胁迫抑制根尖表皮细胞IAA输出模型,即PIN2蛋白和IAA共定位在内化的囊泡内,通过囊泡的循环促进IAA输出。铝抑制细胞膜流动性来阻碍PIN2蛋白内化。硼不仅能促进PIN2载体内吞作用,而且能促进它的分泌,该过程能够修复铝导致的伸长区生长素匮乏。该研究为揭示酸性土壤中供硼缓解铝胁迫机制提供了新的见解。
公司博士研究生陶林为论文第一作者,佛山科学技术学院喻敏教授、bat365官方网站石磊教授和德国波恩大学František Baluška教授为共同通讯作者,佛山科学技术学院课题组吴飞华教授、李学文副教授、冯英明副教授、刘家友讲师、李亚林博士、南京土壤研究所沈仁芳教授、澳大利亚塔斯马尼亚大学Sergey Shabala教授、佛山科学技术学院硕士研究生朱虎及本科生萧晓仪、黄秋雨、郭芷珊、德国波恩大学博士研究生Niloufar Pirayesh、Sakil Mahmud也参与了该项研究。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金的资助。
【英文摘要】
Boron (B) supply alleviates toxic effects of aluminum (Al) on root growth; however, the mechanistic basis of this process remains elusive. This study filled this knowledge gap showing that boron modifies auxin distribution and transport in Al-exposed Arabidopsis roots. In B-deprived roots, Al treatment induced an increase in auxin content in the root apical meristem (MZ) and transition zone (TZ) while in the elongation zone (EZ) auxin content was decreased beyond the level required for adequate growth. These distribution patterns are explained by the fact that basipetal auxin transport from the TZ to EZ was disrupted by Al-inhibited PIN2 endocytosis. Experiments involving modulation of protein biosynthesis by cycloheximide (CHX) and transcriptional regulation by cordycepin (COR) demonstrated that Al-induced increase of PIN2 membrane proteins was depended on the inhibition of PIN2 endocytosis rather than on the transcriptional regulation of PIN2 gene. Experiments reporting profiling of Al3+ and PIN2 proteins revealed that the inhibition of endocytosis of PIN2 proteins was due to Al-induced limitation of the fluidity of the plasma membrane. B supply mediated the turnover of PIN2 endosomes conjugated with IAA and thus restored Al-induced inhibition of IAA transport through the TZ to EZ. Overall, reported results demonstrate that boron supply mediates PIN2 endosome-based auxin transport to alleviate Al toxicity in plant roots.
链接地址:https://10.1111/tpj.16129
审核人:石磊